AdvPulse
AdvPulse is a Subsecond-level Universal, Synchronization-free, and TargetedAdversarial Perturbation.
Intruduce
Features
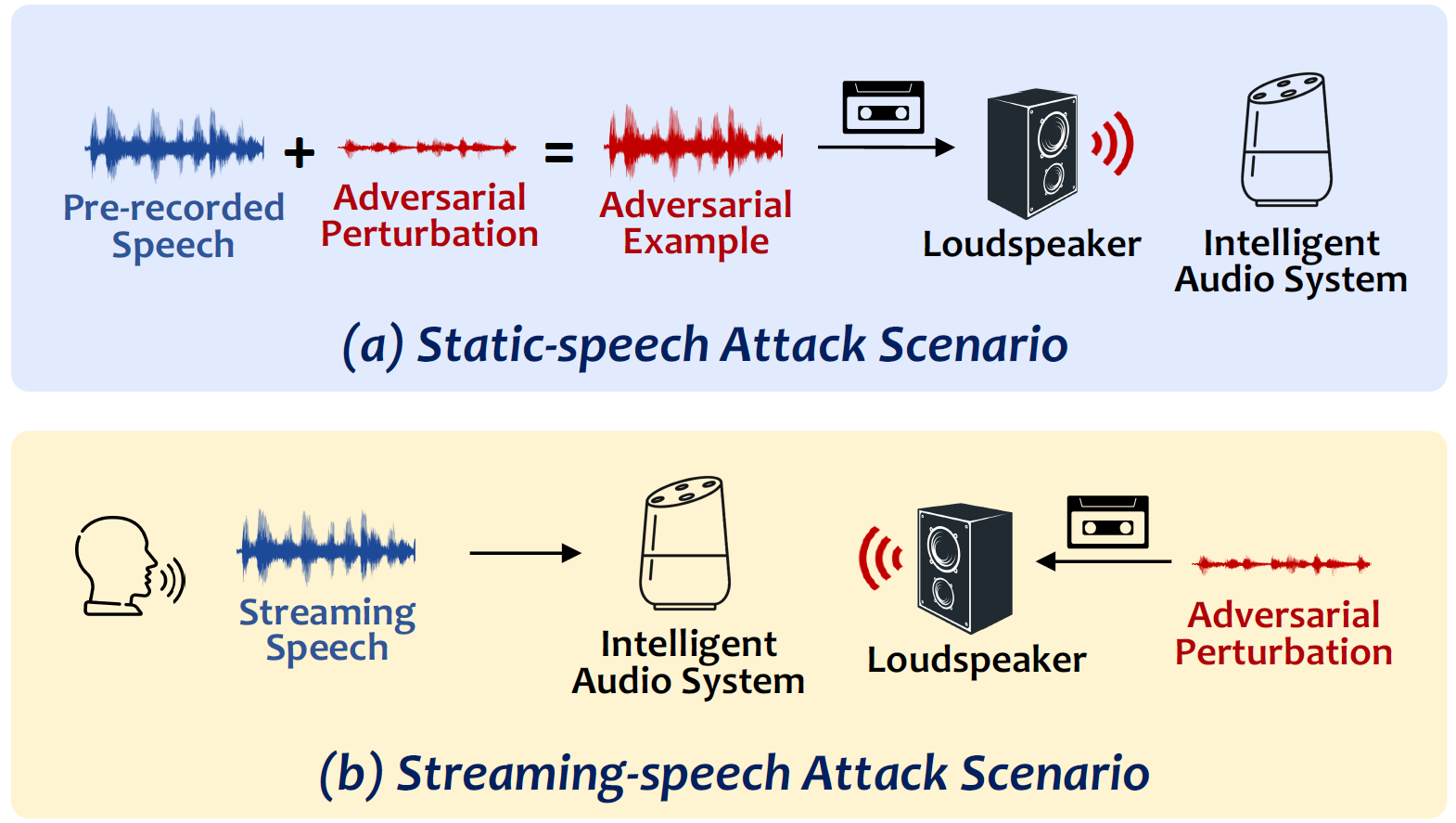
相比于传统的对抗性攻击,AdePulse的特点是通用和非同步,可以面向流式输入实时进行攻击。不过文章并没有说实现黑盒攻击,实验中事先判断目标系统的网络结构为X-VECTOR,即MFCC+DNN+PLDA。

Major Limitations
-
Modifying the Entire Audio Input.
-
Synchronization.
-
Prior Knowledge on the Audio Input.
Main Contributions
- The first work to design a universal, synchronization-free and targeted adversarial attack against intelligent audio systems, particularly for streamingspeech attack scenario (Figure1 (b)), using subsecond adversarial perturbations.
-
We utilize the penalty-based universal adversarial perturbation generation algorithm and optimize the adversarial perturbation over the entire time delay distribution, rendering the attack to be robust to arbitrary streaming audio with varying time delay conditions.
- We propose to use an environmental sound mimicking technique to make the generated subsecond adversarial perturbation resemble situational sound effects (e.g., phone’s notification sound, car horns), making the generated perturbation more inconspicuous to human listeners.
- By incorporating the main sources of distortion occurred during physical playback (i.e., frequency response of speaker and microphone, reflection and reverberation, and ambient noise) into the adversarial perturbation generation process, the effectiveness of adversarial perturbations in physical over-the-air environments can be kept.
- We performed case studies on both speaker recognition and speech command recognition models. Extensive experiments are conducted in both the digital and physical domains, including inside an office, an apartment, and inside-vehicle environments. The results showthat our attack can achieve a high attack success rate in deceiving these models with streaming-speech inputs (e.g., overall 89.2% and 90.3% for speaker recognition and speech command recognition in realistic settings, respectively).
短时非同步 subsecond and Synchronization-free
短噪声
minimizing the following objective function is the fundamental method to generate a adversarial perdurbation.
$$
\begin{align}
& minimize \ \ \ \ \ \mathfrak L\left( f(x+\delta)+\alpha\cdot ||\delta||_2 \right),
& subject to \ \ \ \ \ \ ||\delta||_2<\epsilon,
\end{align}
$$
传统方法需要提前修改整段音频,不能做到流式实时。因此文章提出问题:Is it possible to only modify part of the input signal, desirably a short segment, to fool the model?
Commonly, intelligent audio systems process speech signals into frames, with each frame being handled by the DNN model separately (e.g., the time-delayed neural network structure used in speaker recognition or the convolution neural network structure used in speech command recognition). However, the extracted feature-map of each frame is usually aggregated via a statistic pooling layer or a fully-connected layer before feeding it to the classifier or softmax layer where the final prediction is made. Therefore, by adding adversarial perturbation to only part of the speech signal, the adversary could influence the feature-map extracted from the corresponding speech frames and in turn potentially affect the final recognition result.
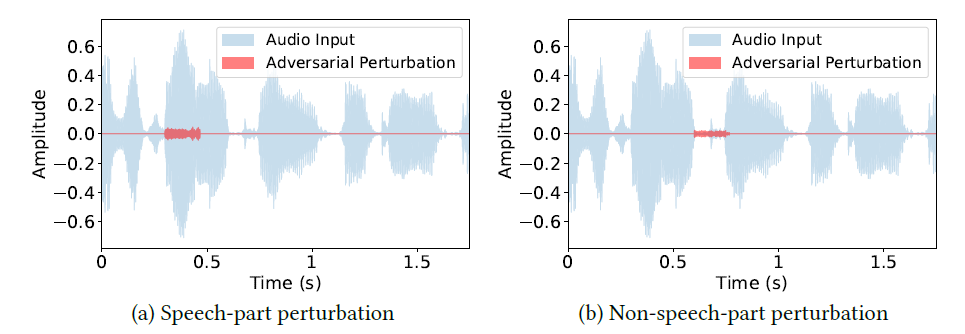
文章提出合理性分析。音频输入给DNN之前要经过分帧处理。每一帧的feature-map在通常要通过静态的池化层进行聚合。因此,把扰动加到部分语音信号就可以影响feature-map,进而影响最终的结果。为了验证这个分析,文章进行了实验验证。实验对Speech-part perturbation和Non-speech-part perturbation分别取0.16s加入扰动都能够成功攻击目标系统,证明短扰动是有效的且是与位置无关的。
ps:我认为这部分的扰动应该是针对于对应段音频产生的,而不是通用的,原文里说的有些模糊。
非同步
使用EOT(Expectation Over Transformation)的方法合成对抗性样本,在生成扰动的过程中加入时间偏移量。与直接求解作用于特定时间戳的对抗性扰动不同,优化一段时间内的损失函数的期望值,使得它加在这段时间内的任何一个地方产生的效果都被优化到。
$$ \begin{align} minimize \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ &\mathbb E\left[ \mathfrak L\left( f\left(x+Shift\left(\delta,\tau\right)\right),y_t\right) + \alpha\cdot ||\delta||_2 \right]&\tau \sim U(0,n-l) \end{align} $$
$n$是音频的总的采样点数,$l$是perturbation的采样点数,$n\gg l$。purturbation $\delta$本身是相当于一个窗口,这个期望的范围就是相当于把窗口从头移动到尾,每一个点都被同等对待(除了首尾),因此这个扰动可以被加到任何地方。
小结
Subsecond和 Synchronization-free的目标就实现了,但是目前还是需要针对于一段已知语音进行提前计算对抗性样本,universal的目标还没实现。
Physically Practical and Universal
Our goal is to find a universal subsecond adversarial perturbation $\delta \in [-1,1]^l$ computed from a relatively small set of training data samples to force the model to recognize arbitrary new audio input (e.g., streaming audio input) as the target label with high probability.
$$ \begin{align} minimize \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ &\mathbb E\left[ \mathfrak L\left( f\left(x+Shift\left(\delta,\tau\right)\right),y_t\right) + \alpha\cdot ||\delta||_2 \right] &\tau \sim U(0,n-l) \ \ \ \ x\sim D \end{align} $$
简而言之,进一步把$x$也纳入优化考量。选择具有代表性的训练样本D训练扰动$\delta$,最后将训练好的应用到D之外的样本中去,实现通用性。以下是训练的算法。
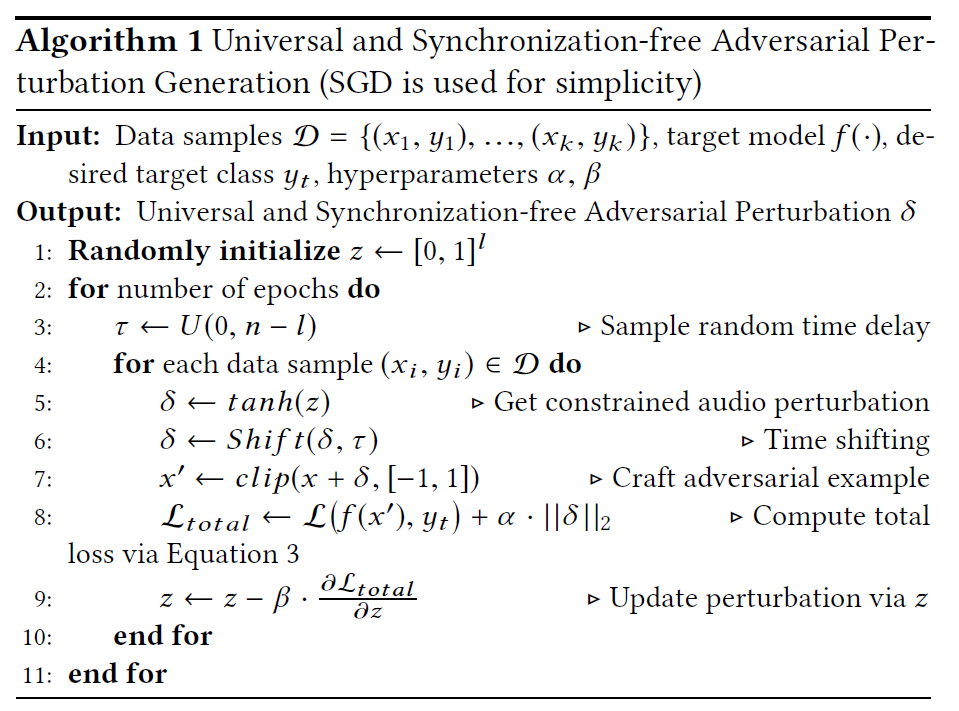
ps:这里是每一个$x$迭代一次$z$,如果是所有$x\in D$迭代完更新一次$z$会不会更能代表整体,相当于使用联合概率分布的期望来作为损失函数。
Robust Adversarial Perturbation for
Over-the-air Attack
环境问题是不可避免的,尤其是对轻微到不易被人察觉的扰动而言。文章通过将以下干扰因素纳入对抗性扰动训练过程,增强了对抗干扰的鲁棒性,从而更好地实现物理攻击。文章依次提出了针对性的解决方法。
- 使用带通滤波器—>扬声器和麦克风限制
- 使用房间冲激响应—>吸收和混响
- 减弱环境噪声的影响—>环境噪声
【待续】
Environmental Sound Mimicking
疑问
X-vector